

Chemistry is all around us
Copyright 2015
This project has been funded with
support from the European Commission
Educational Packages
Chemistry and Environment
Chemistry and energy of the future
Introduction
Energy could be defined as the possibility to carry out work or transfer heat. Two kinds of energy are differentiated: the first is the one we can make use of immediately, e.g the energy produced by our bodies that enable us to perform various activities and is referred to as kinetic energy. The second kind is the energy stored and is referred to as potential energy; for instance, the stored energy in the torch light batteries or the wound up spring which enables the clockwork to operate in a uniform way. Crude oil (petroleum) - It has been formed over millions of years as a product of sea water flora and fauna. Over time the fossils of these living organisms have been covered by multiple layers of mud deposits. Heat and pressure, which these layers formed upon the fossils buried underneath, have created conditions for these plant and animal remnants to be transformed into crude oil.
Crude oil (petroleum) - It has been formed over millions of years as a product of sea water flora and fauna. Over time the fossils of these living organisms have been covered by multiple layers of mud deposits. Heat and pressure, which these layers formed upon the fossils buried underneath, have created conditions for these plant and animal remnants to be transformed into crude oil.
 Coal – This is one of the first non-renewable sources of energy used by humans. They have been formed out of layers of animal and plant residues blanketed by layers of mud and water in marshy areas of land surface. Heat and pressure produced by mud and water layers enabled these remnants to be transformed into coal such as we know it today.
Coal – This is one of the first non-renewable sources of energy used by humans. They have been formed out of layers of animal and plant residues blanketed by layers of mud and water in marshy areas of land surface. Heat and pressure produced by mud and water layers enabled these remnants to be transformed into coal such as we know it today.
 Natural gas – Like above energy sources it has been formed over millions of years deep in the terrestrial core. Natural gas has been formed of putrefied plant and animal residues as concurrent product during formation of crude oil and coal. Natural gas has no color and smell and its molecule is made up of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms.
Natural gas – Like above energy sources it has been formed over millions of years deep in the terrestrial core. Natural gas has been formed of putrefied plant and animal residues as concurrent product during formation of crude oil and coal. Natural gas has no color and smell and its molecule is made up of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms.
 Nuclear energy (uranium) – it is found in the nucleus of an atom. Atoms are tiny particles which make up every object. They consist of electrons, protons and neutrons. The energy that holds atom particles together is actually used by people to turn water into steam which drives turbines producing electricity.
Nuclear energy (uranium) – it is found in the nucleus of an atom. Atoms are tiny particles which make up every object. They consist of electrons, protons and neutrons. The energy that holds atom particles together is actually used by people to turn water into steam which drives turbines producing electricity.
 The rapid growth of energy consumption during the last fifty years has brought the world to the brink of complete depletion of conventional energy sources which puts modern life in great jeopardy. In addition, the energy produced from conventional sources is accompanied by a lot of environmental pollutants and greenhouse gases which increase the greenhouse effect on the entire planet.
Due to these reasons we face the challenge to invent and adopt absolutely novel (renewable) energy sources.
Renewable energy sources are all non-fossil fuels and energy carriers such as solar energy, wind energy, flowing waters energy, geo-thermal energy and bio mass for energy recycling.
The rapid growth of energy consumption during the last fifty years has brought the world to the brink of complete depletion of conventional energy sources which puts modern life in great jeopardy. In addition, the energy produced from conventional sources is accompanied by a lot of environmental pollutants and greenhouse gases which increase the greenhouse effect on the entire planet.
Due to these reasons we face the challenge to invent and adopt absolutely novel (renewable) energy sources.
Renewable energy sources are all non-fossil fuels and energy carriers such as solar energy, wind energy, flowing waters energy, geo-thermal energy and bio mass for energy recycling.
 Solar energy – This is the solar radiation that reaches the earth. Our sun is an extremely powerful energy source, however, man has not invented a method of harnessing this colossal amount of energy. On a cloudless day the amount of energy that reaches the earth at our latitude is in the range of 800-1200 W/m2. Therefore, it is possible to utilize solar energy in two ways: as a heat source and as energy source.
Solar energy – This is the solar radiation that reaches the earth. Our sun is an extremely powerful energy source, however, man has not invented a method of harnessing this colossal amount of energy. On a cloudless day the amount of energy that reaches the earth at our latitude is in the range of 800-1200 W/m2. Therefore, it is possible to utilize solar energy in two ways: as a heat source and as energy source.
 Wind power energy – Wind is air in motion. It is generated by the non-uniform heating of the earth surface. Since it has irregular relief and various water bodies solar radiation is not absorbed uniformly. Whenever the sun shines during the day the air over the ground surface is heated faster as compared to the air over water surfaces. Warm air over the ground surface expands and rises and the colder air over water surface moves in to occupy the place of the warmer air thus generating local winds. During night time winds change directions as the air over ground surface cools down faster than the air over water surface.
Wind power energy – Wind is air in motion. It is generated by the non-uniform heating of the earth surface. Since it has irregular relief and various water bodies solar radiation is not absorbed uniformly. Whenever the sun shines during the day the air over the ground surface is heated faster as compared to the air over water surfaces. Warm air over the ground surface expands and rises and the colder air over water surface moves in to occupy the place of the warmer air thus generating local winds. During night time winds change directions as the air over ground surface cools down faster than the air over water surface.
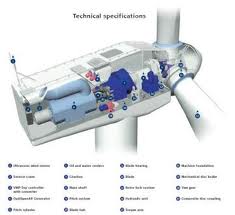
 Wind is a typical source of renewable energy since there will be winds as long as there is sun to shine over earth. Today wind energy is primarily used to generate electricity. Wind generators are the main technical equipment used to convert wind energy into electrical energy. Technically a wind generator consists of a shaft with movable or fixed blades attached to one of its ends. These blades are wing shaped. Wind energy drives the wings which are connected to the axle of electric generator which generates electricity. Wind generators’ efficiency is largely dependent on the location they are installed at. For this purpose estimations of wind velocity and direction over an extended time period are carried out and based on the collected data the exact locations of wind generators are determined.
Wind is a typical source of renewable energy since there will be winds as long as there is sun to shine over earth. Today wind energy is primarily used to generate electricity. Wind generators are the main technical equipment used to convert wind energy into electrical energy. Technically a wind generator consists of a shaft with movable or fixed blades attached to one of its ends. These blades are wing shaped. Wind energy drives the wings which are connected to the axle of electric generator which generates electricity. Wind generators’ efficiency is largely dependent on the location they are installed at. For this purpose estimations of wind velocity and direction over an extended time period are carried out and based on the collected data the exact locations of wind generators are determined.
 Water (hydraulic) energy – Hydraulic energy is non-polluting, renewable and reliable energy source which converts kinetic energy of falling waters into electricity without consuming more water than its natural availability. Water as energy source driving water wheels has been known to man for well over 2000 years. This long period has led to many improvements in the way of obtaining energy.
Mechanical energy needed to turn an electric generator is obtained by means of directing, harnessing and transferring driving water. The quantity of potential energy of water is determined by its discharge and the height from which it falls. In all cases water passes through tubes or chutes and turns a generator by means of a turbine. Most of the hydraulic power stations are built on dam lake walls or at the banks of fast streams or mountain rivers.
Water (hydraulic) energy – Hydraulic energy is non-polluting, renewable and reliable energy source which converts kinetic energy of falling waters into electricity without consuming more water than its natural availability. Water as energy source driving water wheels has been known to man for well over 2000 years. This long period has led to many improvements in the way of obtaining energy.
Mechanical energy needed to turn an electric generator is obtained by means of directing, harnessing and transferring driving water. The quantity of potential energy of water is determined by its discharge and the height from which it falls. In all cases water passes through tubes or chutes and turns a generator by means of a turbine. Most of the hydraulic power stations are built on dam lake walls or at the banks of fast streams or mountain rivers.
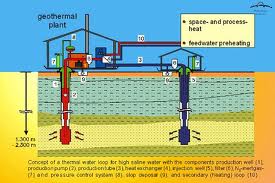
 Geothermal energy – It may be used as an effective heat source, for example in supplying heat for green houses, however, the consumer should be in the vicinity of this geo-thermal heat source. Geothermal energy that is the heat coming from earth depths is an important energy source which features considerable ecological and economic advantages as compared to fossil fuel energy and nuclear energy.
Geothermal energy – It may be used as an effective heat source, for example in supplying heat for green houses, however, the consumer should be in the vicinity of this geo-thermal heat source. Geothermal energy that is the heat coming from earth depths is an important energy source which features considerable ecological and economic advantages as compared to fossil fuel energy and nuclear energy.
 Dry steam power plants
Dry steam power plants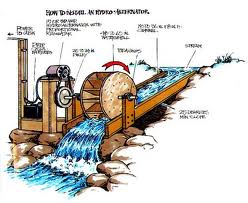 Sea waves energy – Production of electricity from ocean energy utilizes tidal energy, wave energy and the conversion of ocean thermal energy, ocean streams and the change in water salinity.
Sea waves energy – Production of electricity from ocean energy utilizes tidal energy, wave energy and the conversion of ocean thermal energy, ocean streams and the change in water salinity.
 Tidal energy
Tidal energy Wave energy
Wave energy Biodiesel – Biodiesel is a liquid fuel made up of fatty acid alkyl esters, fatty acid methyl esters (FAME), or long-chain mono alkyl esters. It is produced from renewable sources such as fresh and used vegetable oils and animal fats and is a cleaner-burning replacement for petroleum-based diesel fuel. It is nontoxic and biodegradable. Biodiesel has physical properties similar to those of petroleum diesel:
Biodiesel – Biodiesel is a liquid fuel made up of fatty acid alkyl esters, fatty acid methyl esters (FAME), or long-chain mono alkyl esters. It is produced from renewable sources such as fresh and used vegetable oils and animal fats and is a cleaner-burning replacement for petroleum-based diesel fuel. It is nontoxic and biodegradable. Biodiesel has physical properties similar to those of petroleum diesel:
| Biodiesel's Physical Characteristics | |
| Specific gravity | 0.88 |
| Kinematic viscosity at 40°C | 4.0 to 6.0 |
| Cetane number | 48 to 65 |
| Higher heating value, Btu/gal | 127,042 |
| Lower heating value, Btu/gal | 118,170 |
| Density, lb/gal at 15.5°C | 7.3 |
| Carbon, wt% | 77 |
| Hydrogen, wt% | 12 |
| Oxygen, by dif. wt% | 11 |
| Boiling point, °C | 315-350 |
| Flash point, °C | 100-170 |
| Sulfur, wt% | 0.0 to 0.0024 |
| Cloud point, °C | -3 to 15 |
| Pour point, °C | -5 to 10 |
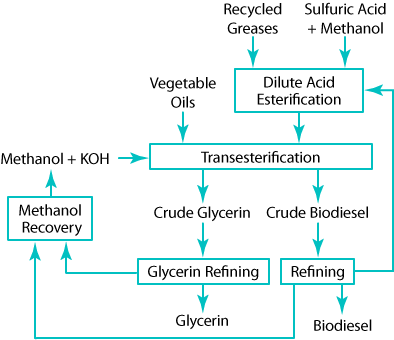
Block schematic of biodiesel production process.
 Bioethanol – It appears to be a feasible alternative to petrol. Biomethanol is produced from vegetable species which have been known to man for centuries on end such as sugar cane, corn and barley. Bioethanol is a renewable energy source, a substitute of and an additive to conventional petrol. It not only features higher octane number allowing for greater efficiency of the engine, but also has lower harmful emissions. Bioethanol has no toxic ingredients, contains no sulphur and is produced without any wastes.
Bioethanol – It appears to be a feasible alternative to petrol. Biomethanol is produced from vegetable species which have been known to man for centuries on end such as sugar cane, corn and barley. Bioethanol is a renewable energy source, a substitute of and an additive to conventional petrol. It not only features higher octane number allowing for greater efficiency of the engine, but also has lower harmful emissions. Bioethanol has no toxic ingredients, contains no sulphur and is produced without any wastes.
 Adding bioethanol to fuel causes more effective burning in internal combustion engines.However, it is not recommendable to use this additive in a voluntary way since larger concentrations could harm the car engine. Most governments have taken regulatory measures which rule that bioethanol be used within the limit of 2% that is far from the engine damage threshold and in the same time raises engine efficiency and lowers harmful emissions.
Adding bioethanol to fuel causes more effective burning in internal combustion engines.However, it is not recommendable to use this additive in a voluntary way since larger concentrations could harm the car engine. Most governments have taken regulatory measures which rule that bioethanol be used within the limit of 2% that is far from the engine damage threshold and in the same time raises engine efficiency and lowers harmful emissions.
Exercises
Step 1